Landing Pages
What is a Landing Page?
Section titled “What is a Landing Page?”Unlike traditional websites that offer multiple navigation paths, a landing page is a single, conversion-focused page.
It serves as an entry point for visitors coming from email campaigns, ads, search engines, or social media.
Possible goals:
- Lead generation
- Selling a product
- Event registration
- Subscription to a service
- App installation
Types of Landing Pages
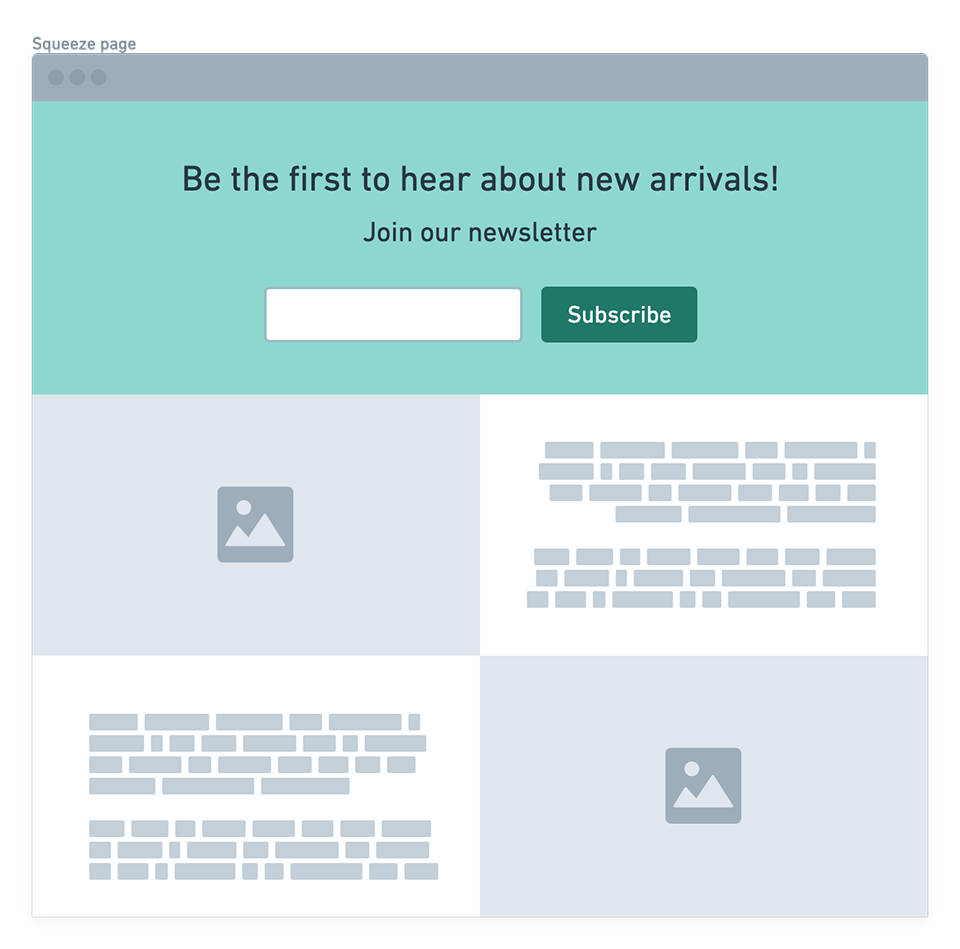
Section titled “Types of Landing Pages”Squeeze Page
Section titled “Squeeze Page”- Goal: collect leads via a simple form
- Few input fields to maximize completion rate
- Often used to offer premium content (white papers, templates)
- Main KPI: form completion rate
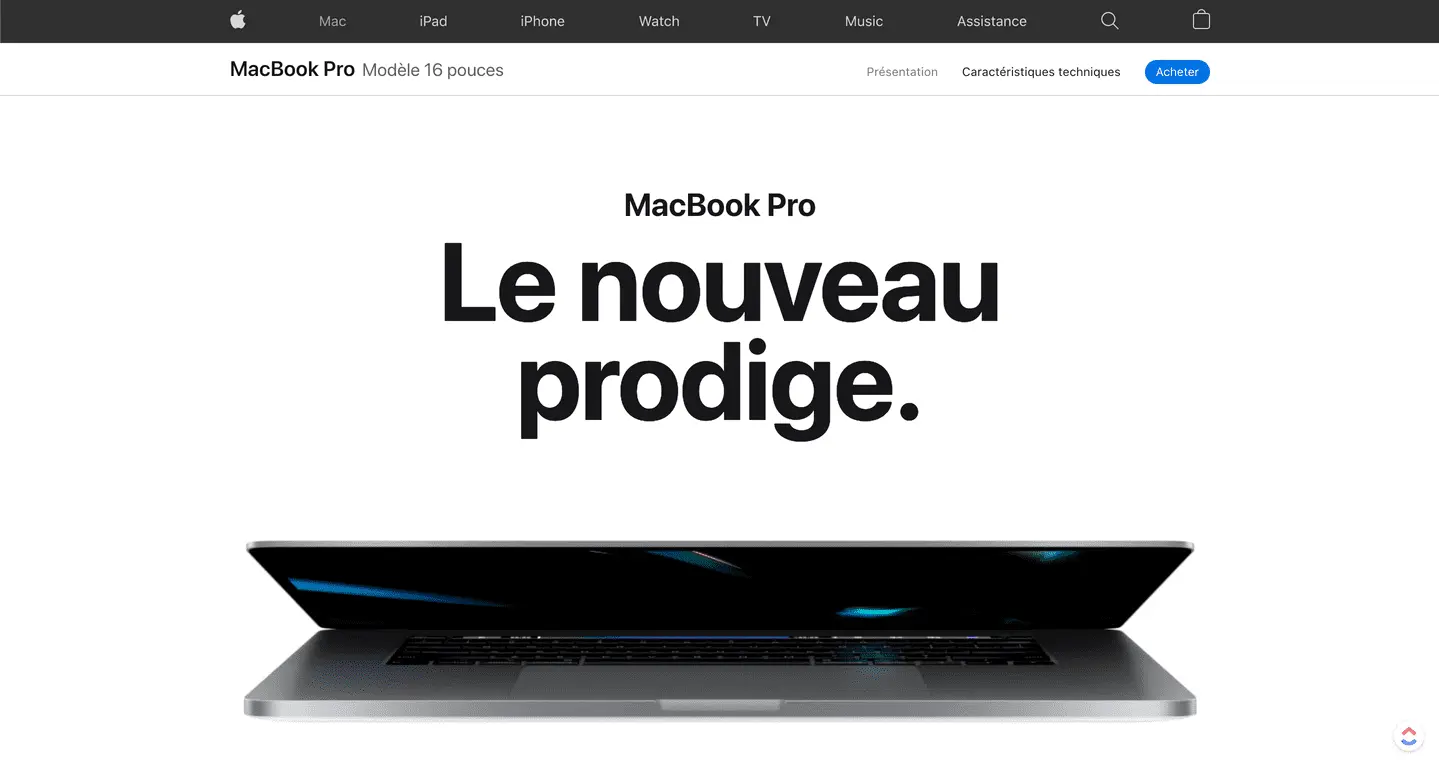
Sales Page
Section titled “Sales Page”- Aims to sell a specific product or service
- Clear value proposition right in the hero section
- Includes testimonials, reviews, and trust elements
- Strong, high-contrast call-to-action
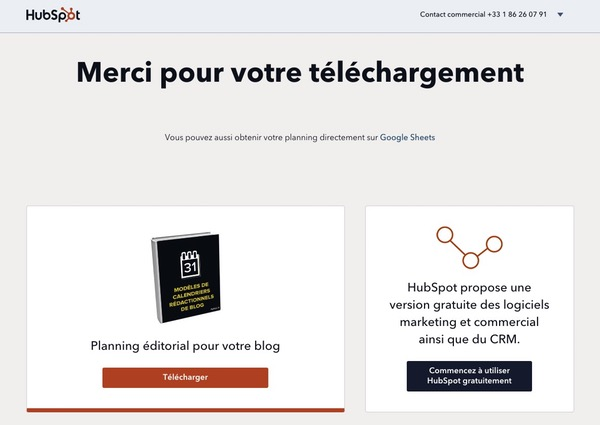
Thank You Page
Section titled “Thank You Page”- Shown after a user action (purchase, signup, reservation)
- Confirms the process was completed
- Can introduce cross-sell or upsell suggestions
- A key step for customer experience
Splash Page
Section titled “Splash Page”- Intro page before accessing the main website
- Lets users choose language, region, or content type
- Sets up brand identity
- Must be fast and skippable to avoid frustration

App Download Page
Section titled “App Download Page”- Optimized to encourage installations
- Visual presentation via mockups
- Highlights key features
- Clear, visible download buttons
Landing Page vs Website
Section titled “Landing Page vs Website”| Website | Landing Page |
|---|---|
| Set of multiple pages | Single page |
| Several goals | One specific goal |
| Multiple navigation paths | Limited or no navigation |
| Multiple call-to-actions | Single or very focused CTA |
Designing an Effective Landing Page
Section titled “Designing an Effective Landing Page”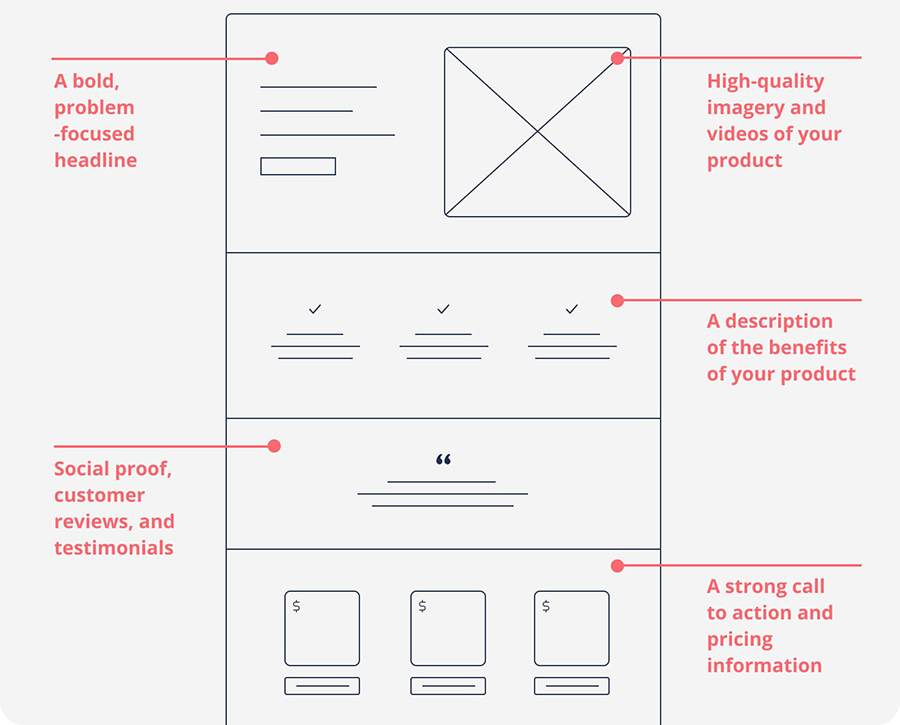
Design
Section titled “Design”- Matches visual brand identity
- Responsive and easy to read
- Clear, structured layout
Content
Section titled “Content”- Clear and immediate value proposition
- Catchy title and benefit-driven copy
Call-to-Action (CTA)
Section titled “Call-to-Action (CTA)”- Action verbs in imperative form
- Strong contrast with background
- Large, clickable area
- Placed near sales arguments
Navigation
Section titled “Navigation”- “Funnel” approach (no navigation) for fast conversions
- Simplified navigation for higher-involvement products
Credibility
Section titled “Credibility”- Testimonials, reviews, client logos
- Builds trust and reduces hesitation
Measuring Performance
Section titled “Measuring Performance”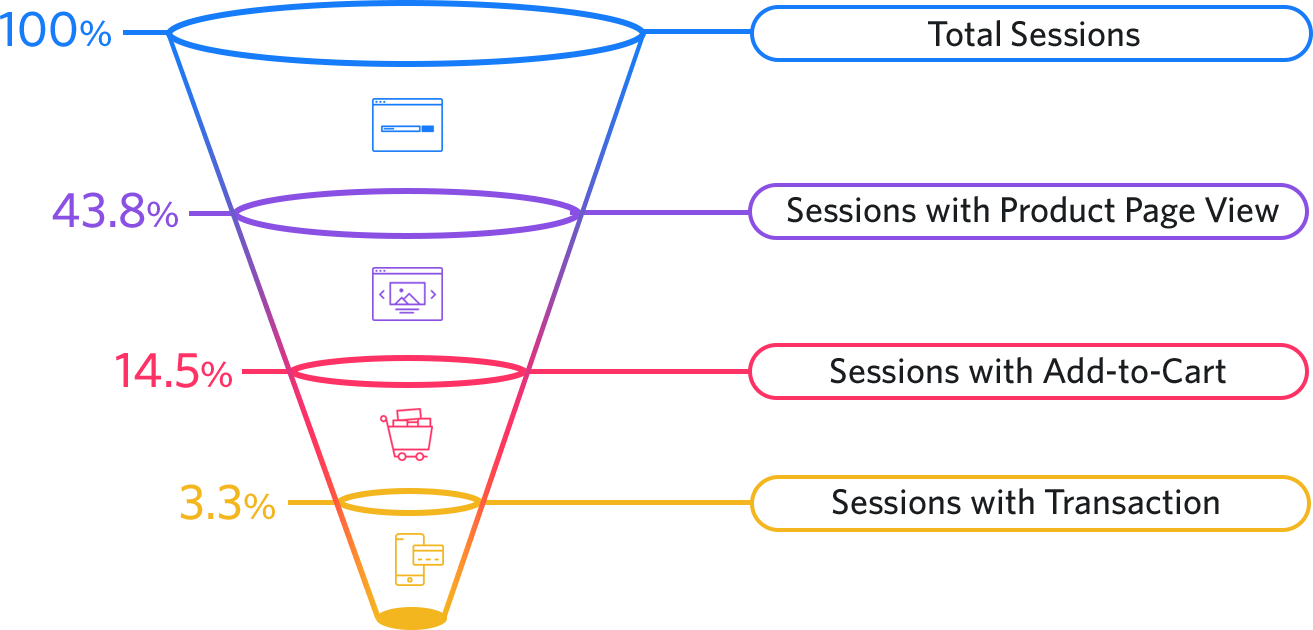
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Conversion rate
- Number of conversions
- Bounce rate
- Time spent on page
- Traffic sources
- A/B test results
Analytics tools: Google Analytics, Microsoft Clarity, Hotjar
Key Takeaways
Section titled “Key Takeaways”- A landing page = clear goal + targeted content + simplified path
- Its purpose is to quickly persuade and guide toward a specific action
- Its effectiveness depends on continuous measurement and regular optimization