Introduction to Marketing
Introduction
Section titled “Introduction”Marketing is a set of actions aimed at understanding consumer needs and responding to them effectively.
It relies on:
- Influence strategies
- Market analysis
- Target segmentation
- Offer positioning and distribution
Types of Marketing Strategies
Section titled “Types of Marketing Strategies”Outbound Marketing (Traditional)
Section titled “Outbound Marketing (Traditional)”- Messages pushed to the consumer
- Examples: TV ads, radio, billboards, cold calls
- Less targeted, more intrusive, easier to deploy
Inbound Marketing (Modern)
Section titled “Inbound Marketing (Modern)”- Attracting customers through relevant content
- Examples: SEO, social media, newsletters
- More engaging, but requires time and effort
Offline vs Digital Marketing
Section titled “Offline vs Digital Marketing”Offline Marketing
Section titled “Offline Marketing”- Physical media: billboards, print, TV, etc.
- Reaches audiences not connected online
- More tangible and emotionally driven
Digital Marketing
Section titled “Digital Marketing”- Online channels: websites, emails, social media
- Wide reach, precise targeting, easy to measure
- Includes SEO, SEA, affiliate, influencer marketing
Building a Marketing Strategy
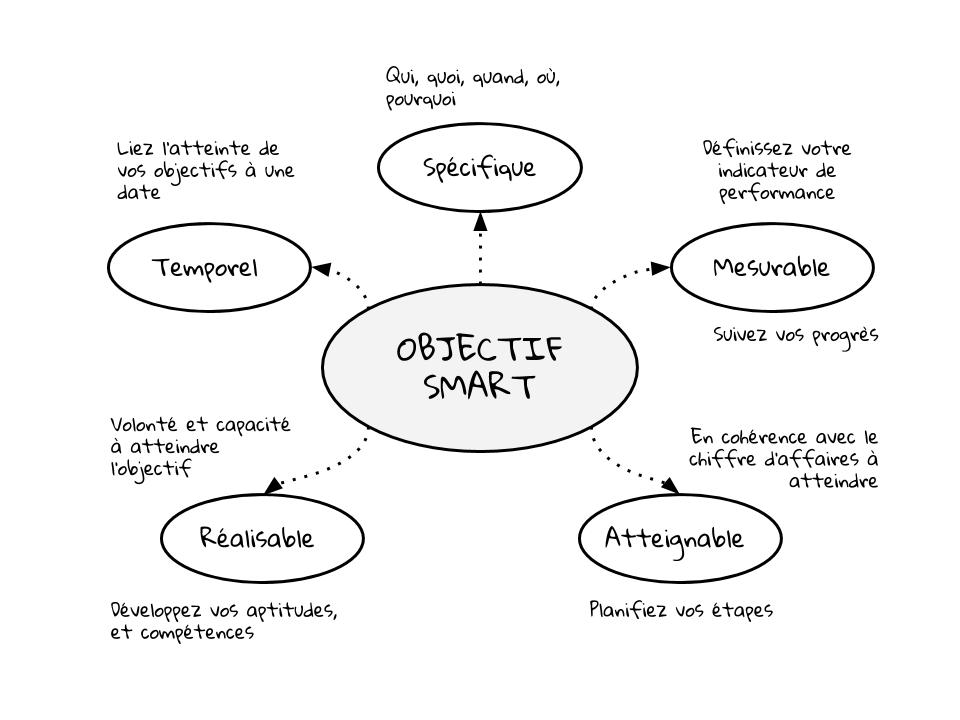
Section titled “Building a Marketing Strategy”SMART Objectives
Section titled “SMART Objectives”- Specific
- Measurable
- Achievable
- Realistic
- Time-bound
TOMSTER Method
Section titled “TOMSTER Method”- Target: define the audience
- Objectives: set goals
- Message: define editorial line
- Strategy: plan the actions
- Technology: choose the right tools/channels
- Evaluating: track KPIs
- Resources: assign budget/team
Identifying Target Audiences
Section titled “Identifying Target Audiences”Through segmentation:
- Demographic
- Psychological
- Behavioral
- Geographic
Choosing a Positioning
Section titled “Choosing a Positioning”- The brand’s image in the consumer’s mind
- Helps stand out from competitors
The Marketing Mix (4P + 3P)
Section titled “The Marketing Mix (4P + 3P)”The 4Ps
Section titled “The 4Ps”- Product: offer, quality, packaging, after-sales
- Price: pricing strategy, discounts, positioning
- Place: distribution channels (online, retail)
- Promotion: communication, advertising, influencers
3 Additional Ps
Section titled “3 Additional Ps”- Process: smooth customer journey (UX/UI)
- People: human relationship, staff image
- Physical Evidence: reviews, testimonials, legal mentions
Measuring with KPIs
Section titled “Measuring with KPIs”Key Performance Indicators help:
- Track performance
- Adjust strategies
- Identify new opportunities

Example: Increase Instagram post reach by 25% in 6 months
Example KPIs
Section titled “Example KPIs”| KPI | Why it matters |
|---|---|
| Click-through rate (CTR) | Measure ad effectiveness |
| Conversion rate | Track sales or signups |
| Reach / Impressions | Evaluate visibility |
| Bounce rate | Assess content relevance |
| Leads / Revenue | Reflect business objectives |
Planning a Marketing Campaign
Section titled “Planning a Marketing Campaign”- Define the target and goal
- Choose suitable channels
- Create content (slogan, visuals, CTA)
- Schedule and publish
- Measure results (KPIs)
- Adjust based on performance
Examples of Successful Campaigns
Section titled “Examples of Successful Campaigns”- Netflix – Streamberry (Black Mirror): immersive storytelling
- Lego: co-creation with its community
- Jul x Oasis: viral music campaign
- Marvel: cross-media marketing (TV reports, etc.)
Key Takeaways
Section titled “Key Takeaways”- Marketing is based on customer listening and continuous adjustment
- A strong strategy = clear objectives + precise targeting + data-driven execution